Ever wondered why people use the terms "race" and "ethnicity" interchangeably but still feel like there's a deeper meaning behind them? Well, buckle up, because we're diving headfirst into this fascinating topic. The difference between race and ethnicity is more than just words—it's about identity, culture, and history. Whether you're a student, researcher, or simply curious, understanding these terms can change the way you see the world. So, let's get started!
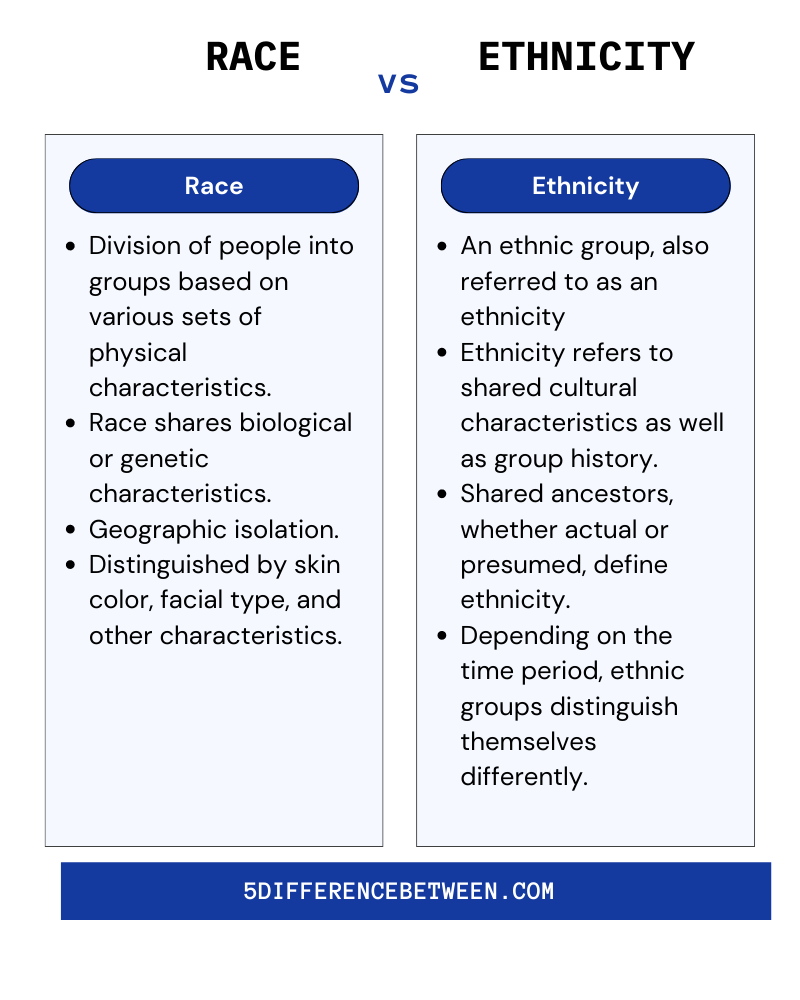
When we talk about race and ethnicity, it’s easy to get confused. They both deal with how people identify themselves and how society categorizes them. But here's the kicker: race is more about physical traits, while ethnicity dives deeper into cultural practices, traditions, and ancestry. It’s like comparing the color of your skin to the stories your grandparents told you growing up.
This article isn’t just about definitions—it’s about exploring the nuances of identity in a globalized world. We’ll break down the differences, highlight key examples, and even throw in some stats to keep things real. By the end, you’ll have a clearer understanding of why these concepts matter so much in today’s society.
Read also:Everything You Need To Know About Using Tampons A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the Basics: What is Race?
Let’s start with the basics. Race is often defined as a classification of humans based on physical characteristics, like skin color, facial features, and hair texture. Think of it as a broad brushstroke that groups people together based on what they look like. But here’s the thing—race isn’t just about biology; it’s also deeply tied to societal perceptions and historical contexts.
In many societies, race has been used to create divisions, often leading to discrimination and inequality. For example, the concept of race was weaponized during colonial times to justify slavery and oppression. Today, race continues to shape how people are treated in various systems, from healthcare to education.
Key Characteristics of Race
- Biological traits like skin color, eye shape, and hair texture.
- Historically influenced by scientific theories (some now debunked).
- Often used to categorize people in census data and government statistics.
But here’s where it gets interesting—race isn’t set in stone. What one society considers a racial category might not exist in another. For instance, in the U.S., "Caucasian" is a common racial label, but in Europe, it might not carry the same meaning. It’s all about perspective and context.
What is Ethnicity? A Deeper Dive
Now let’s shift gears and talk about ethnicity. Unlike race, ethnicity focuses on cultural identity. It’s all about where you come from, the traditions you follow, and the language you speak. Think of it as a tapestry woven with threads of heritage, religion, and community.
Ethnicity is personal. It’s the food your mom makes on special occasions, the songs you grew up listening to, and the holidays you celebrate. It’s what makes you, well, YOU. And while race might tell you what you look like, ethnicity explains who you are inside.
Key Characteristics of Ethnicity
- Cultural practices, such as language, religion, and traditions.
- Often tied to geographical regions or ancestral origins.
- More fluid and adaptable than race, as people can adopt new cultural identities.
For example, someone might identify as racially "Black" but ethnically "African American" or "Nigerian." The beauty of ethnicity lies in its complexity—it’s not a one-size-fits-all label.
Read also:Cousins Maine Lobster Net Worth A Deep Dive Into Their Success Story
The Historical Context of Race and Ethnicity
To truly understand the difference between race and ethnicity, we need to look back at history. The concept of race gained traction during the 18th and 19th centuries, when European scientists and philosophers tried to classify humans into distinct groups. Unfortunately, this led to some pretty harmful ideas, like the belief in racial hierarchies.
Ethnicity, on the other hand, has been around for centuries. Ancient civilizations identified themselves based on shared cultures and languages. Even today, ethnic groups around the world celebrate their unique identities through festivals, art, and music.
Key Historical Milestones
- The rise of racial science in the 18th century.
- The impact of colonization on ethnic identities.
- The civil rights movement’s fight against racial discrimination.
History shows us that race and ethnicity aren’t just abstract concepts—they’re deeply intertwined with power dynamics and social structures. Understanding this context helps us appreciate why these terms matter so much today.
How Do Race and Ethnicity Intersect?
Here’s where things get really interesting. Race and ethnicity aren’t mutually exclusive—they often overlap in fascinating ways. For example, someone might be racially "Asian" but ethnically "Korean." Or they could be racially "Hispanic" but ethnically "Mexican American." See how it works?
This intersectionality is what makes identity so complex. People can belong to multiple racial and ethnic groups, and their experiences will vary depending on how these identities interact. It’s like a puzzle with countless pieces, each one adding depth and richness to the whole picture.
Examples of Intersectionality
- African Americans who identify as both racially "Black" and ethnically "Southern."
- Indigenous Australians who are racially "Aboriginal" but ethnically tied to specific tribes.
- Mixed-race individuals who draw from multiple ethnic backgrounds.
These examples highlight the fluidity of identity. Race and ethnicity aren’t fixed—they evolve over time, influenced by personal experiences, societal changes, and global interactions.
The Role of Society in Shaping Identity
Society plays a huge role in how we perceive race and ethnicity. From media portrayals to institutional policies, external forces shape how we see ourselves and others. For instance, Hollywood has long been criticized for its narrow depictions of racial and ethnic groups. But the tide is turning, with more diverse voices gaining visibility in mainstream media.
In education, the way race and ethnicity are taught can either reinforce stereotypes or promote understanding. Curricula that incorporate multicultural perspectives help students appreciate the richness of human diversity. It’s all about creating spaces where everyone feels seen and heard.
Impact on Daily Life
- Racial profiling in law enforcement.
- Ethnic stereotyping in advertising and media.
- Cultural appropriation vs. appreciation in fashion and art.
These issues highlight the importance of being mindful about how we use race and ethnicity in everyday conversations. It’s not just about being politically correct—it’s about showing respect and empathy for others’ experiences.
Data and Statistics: The Numbers Behind Race and Ethnicity
Let’s talk numbers. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the racial and ethnic makeup of the population is constantly changing. For example, the Hispanic population is projected to grow significantly over the next few decades. Meanwhile, Asian Americans are becoming one of the fastest-growing ethnic groups in the country.
Globally, the picture is even more diverse. Countries like Canada and Australia have embraced multiculturalism as a core part of their national identity. In contrast, some nations still struggle with xenophobia and ethnic tensions. The data paints a complex portrait of a world in flux.
Key Statistics
- By 2060, the U.S. minority population is expected to surpass 50%.
- India is home to over 2,000 ethnic groups, making it one of the most diverse countries in the world.
- Europe’s immigrant population has doubled in the last 20 years, driven by economic migration and refugee crises.
These stats remind us that race and ethnicity aren’t static—they’re living, breathing concepts that reflect the ever-changing nature of our world.
Challenges in Defining Race and Ethnicity
Defining race and ethnicity isn’t easy. There’s no universal agreement on what constitutes a racial or ethnic group. Some argue that race is a social construct with no biological basis, while others believe it still holds some validity. Meanwhile, ethnicity can be equally tricky to pin down, especially for people with mixed backgrounds.
Another challenge is the stigma attached to certain racial and ethnic labels. For example, the term "minority" can perpetuate feelings of inferiority, even though it’s meant to describe numerical representation. It’s all about finding language that’s both accurate and respectful.
Solutions for Better Understanding
- Encourage open dialogue about race and ethnicity in schools and workplaces.
- Support research that challenges outdated stereotypes and assumptions.
- Promote policies that celebrate diversity and inclusion.
By addressing these challenges head-on, we can create a more inclusive society where everyone feels valued.
Why Does the Difference Between Race and Ethnicity Matter?
Understanding the difference between race and ethnicity isn’t just an academic exercise—it has real-world implications. From healthcare to politics, these concepts shape how we interact with each other and the systems around us. For example, racial disparities in healthcare outcomes are a major concern, with minority groups often receiving lower-quality care.
Ethnicity, too, plays a crucial role in shaping policies and programs. Language access, cultural competency training, and targeted outreach efforts all rely on a nuanced understanding of ethnic diversity. When we get it right, the benefits are enormous—better health outcomes, stronger communities, and a more equitable society.
Real-World Applications
- Healthcare providers using ethnic data to tailor treatment plans.
- Companies implementing diversity initiatives to attract top talent.
- Governments designing policies that address the needs of specific ethnic groups.
These examples show how race and ethnicity aren’t just theoretical concepts—they’re practical tools for creating positive change.
Conclusion: Embracing Diversity in All Its Forms
So, what have we learned? Race and ethnicity are two distinct but interconnected concepts that shape our identities and experiences. While race focuses on physical traits, ethnicity delves into cultural practices and traditions. Both are vital for understanding the rich tapestry of human diversity.
As we’ve seen, the difference between race and ethnicity matters—not just for individuals, but for society as a whole. By embracing this complexity, we can build a world where everyone feels seen, heard, and valued. So, what’s next? Leave a comment below sharing your thoughts, or check out our other articles for more insights into the world of identity and culture. Together, let’s keep the conversation going!
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Basics: What is Race?
- What is Ethnicity? A Deeper Dive
- The Historical Context of Race and Ethnicity
- How Do Race and Ethnicity Intersect?
- The Role of Society in Shaping Identity
- Data and Statistics: The Numbers Behind Race and Ethnicity
- Challenges in Defining Race and Ethnicity
- Why Does the Difference Between Race and Ethnicity Matter?
- Conclusion: Embracing Diversity in All Its Forms